Emma Green speaks to the lead investigator behind research in Berlin to find out whether graphic medicine can ease pre-surgery anxiety and educate patients

In a study involving more than 120 patients, comic-style illustrations were used to ease anxiety over upcoming heart procedures (Credit: Steven Miller/Flickr)
Before undergoing surgery, patients must be fully informed about what the procedure entails, yet the complex nature of the content provided means they often feel overwhelmed. New research shows that comic-style information – known as graphic medicine – can be helpful. Practical Patient Care writer Emma Green speaks to the lead investigator behind these findings about their wider implications.
The aim of an informed consent procedure is to ensure that patients can make an autonomous decision.
This involves the provision of details about the procedure, including the associated risks and benefits.
Due to the complex nature of certain treatments, as well as the anxiety associated with them, patients often struggle to fully understand the steps involved.
Researchers from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, one of the largest university hospitals in Europe, were inspired by the idea that a picture is worth a thousand words and wanted to test whether comic-style information might be more easily digested by patients.
The team focused on cardiac catheterisation, the most common procedure in the field of cardiology.
The provision of medical information within a comic format is seemingly an unusual choice but was a carefully considered decision by researchers.
A key factor was the realisation of the ineffectiveness of the current method of informing patients about cardiac catheterisation.
“We realised that patients were not as well prepared as we would wish them to be, even though the physician was communicating all aspects of the investigation and they were receiving a standard written consent form,” says Anna Brand, lead investigator and cardiologist at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin.
“They still had several questions at the beginning of the procedure.”
Graphic medicine for pre-surgery anxiety
Researchers looked for alternative approaches to presenting the information.
They stumbled upon graphic medicine – a growing field in the US and France, in particular – which uses comics to communicate information to patients and their families, as well as educating students.
“We thought that comics might help in the informed-consent procedure because text is too complex for patients who lack knowledge of their disease and its treatment,” says Brand.
Together with Alexandra Hamann, a science communication specialist, Brand and Professor Verena Stangl from the medical department, division of cardiology and angiology on Campus Charité Mitte, developed a storyboard based on the standard consent form for cardiac catheterisation.
The team went to great lengths to optimise the likelihood of it being effective for patients.
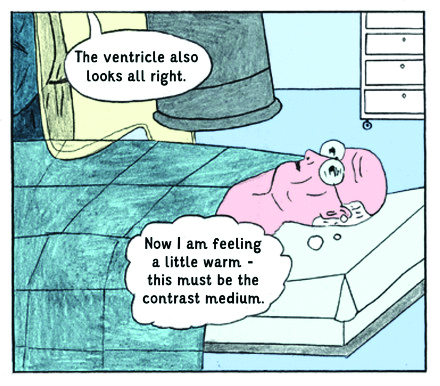
“We didn’t only want to have the comic but we really wanted to test its effects,” says Brand.
“Is it useful? Do patients understand more? Does the comic help them to feel less anxious?”
As cardiac catheterisation is so routine within cardiology, Brand was acutely aware of how patients felt about it.
“A lot of patients are very worried about the procedure and they expect a larger operation than just an invasive coronary angiography,” she explains.
Researchers hoped that the comic-style information might be a useful way of reducing anxiety as well as informing them about the treatment.
How was comic-style information tested?
In order to put the comic-style booklet to the test, the team recruited 121 individuals scheduled to undergo cardiac catheterisation.
Patients received either the standard informed consent procedure or the standard informed consent with additional comic-style information.
Using a range of questionnaires administered before and after the provision of the information, researchers assessed levels of comprehension and anxiety in addition to the satisfaction with the consent process.
The comic-style booklet was found to be significantly superior to the standard information.
“Patients who read the comic before the procedure could answer 12 of 13 questions correctly on the multiple-choice test that was assessing comprehension,” explains Brand.
“We were even more surprised by the limited value of the standard information because patients who read a text which contained all the information for the test only answered 9 of those 13 questions.”
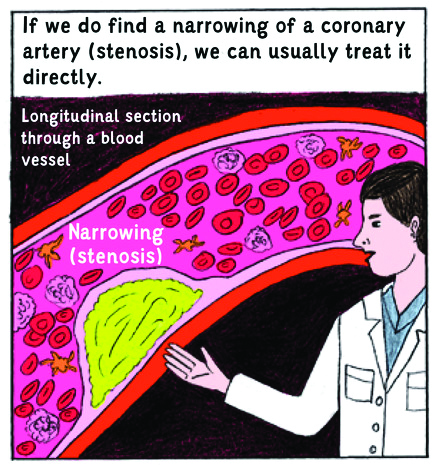
There were also positive emotional effects of the comic-style information for participants.
“Patients in the comic-style information group also reported feeling less anxious after their informed consent procedure,” says Brand.
“Patients even expressed more anxiety following the standard informed consent, which was something that was really surprising to us.”
Perhaps most surprising was the high level of acceptance of this format in light of it being relatively novel.
“Approximately 72% of participants were satisfied with the comic-based information booklet and reported feeling well-prepared for cardiac catheterisation,” explains Brand.
“This is compared with only 41% in the standard informed consent group.”
Benefits for all patients
Comic-style information is clearly effective, but are there certain types of patients who stand to benefit the most from this format?
“What we saw was that patients without any professional education had poorer results on the multiple-choice test that was assessing patient comprehension than those with more education,” says Brand.
“Given that the official standard form is very complex and beyond the literacy level of many patients, I could imagine these individuals maybe benefit the most from comic-style information.”
That doesn’t mean that comic-style information is not suitable for those with high educational levels.
“On the other hand, the patients that had a higher university degree were also happy to receive the comic because, although they were educated, they didn’t have knowledge of this particular medical field,” notes Brand.
“They also said that they really liked this form of patient information, so comic-style information can be used for all different types of patients.”
Researchers were surprised by this as they expected that more highly educated patients might find it too simplistic.
“More than 95% said that this was not the case; they felt better informed and were happy with the comic-style consent form,” says Brand.
“The high levels of acceptance of this format is beneficial because it means that all patients can be provided with this style of consent form, rather than singling out patients based upon their educational level.
The upshot
There are a number of benefits of using comics for both patients and healthcare professionals.
“Sometimes patients do not want to ask, or they forget what they have been told,” explains Brand.
“It is also very useful for us medical doctors because it allows you to convey very complex aspects of the disease or of the procedure in an easy manner.”
As a result of the research findings, cardiologists working at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin have already changed their informed
consent procedure.
“We now use the comic-style information form as standard procedure for patients receiving a coronary angiography,” says Brand.
The team are also very keen to take their work forward.
“We see elderly or foreign patients that may struggle more with the standard informed consent procedure,” explains Brand.
“We would like to test comic-style information for these types of patients, as well as for other procedures within the cardiovascular field.”
This article first appeared in Issue 24, 2019 of Practical Patient Care. The full publication can be viewed here.
